The Importance of Cybersecurity is undeniable in today’s digital world. As cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks, prioritizing the Importance of Cybersecurity ensures protection for individuals, businesses, and governments. This blog explores how the Importance of Cybersecurity mitigates risks like ransomware and safeguards critical data.
What is Cybersecurity?

Cybersecurity refers to the practice of defending devices, networks, systems, and data from unauthorized access or malicious attacks. It aims to ensure three core principles:
- Confidentiality: Data is accessible only to authorized users.
- Integrity: Data remains accurate and unaltered unless by authorized actions.
- Availability: Systems and data are accessible when needed.
By focusing on these principles, cybersecurity helps maintain trust in digital systems and ensures the smooth functioning of essential services.
To better understand the growing importance of cybersecurity in our society, check out this insightful article on its critical role in the modern world. Link
Why the Importance of Cybersecurity Matters

1. Protecting Personal Data
In the modern world, individuals store sensitive information online, such as financial details, medical records, and personal identities. Cybersecurity prevents unauthorized access to this data, protecting individuals from identity theft and financial fraud. The Importance of Cybersecurity lies in preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information like financial records and medical histories.
2. Safeguarding Businesses
Companies rely heavily on digital platforms for operations, data management, and customer interaction. Cybersecurity ensures the safety of their systems, protecting them from ransomware, phishing, and data breaches. A single breach can cause financial losses and damage customer trust.
3. Ensuring National Security
Governments store critical data and control essential infrastructure such as power grids, healthcare systems, and defense networks. Cybersecurity helps protect these assets from cyber terrorism and state-sponsored attacks, safeguarding public safety and national interests.
4. Supporting Business Continuity
Cyberattacks can disrupt operations by crippling systems or stealing sensitive data. By implementing strong cybersecurity measures, businesses can ensure operational continuity, minimize downtime, and protect their revenues.
5. Enabling Financial Safety
The growth of e-commerce and online banking has opened doors for financial fraud. Cybersecurity safeguards online transactions through encryption and authentication, ensuring secure payment systems.
Common Cyber Threats Highlighting the Importance of Cybersecurity

1. Malware
Malware refers to malicious software like viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware. These programs disrupt systems, steal sensitive data, or encrypt files for ransom. Malware often infiltrates devices through phishing emails or unsecured downloads.
2. Phishing
Phishing scams involve fraudulent emails or messages designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information. These attacks often target login credentials, credit card numbers, and other personal data.
3. Ransomware
Ransomware encrypts a victim’s data and demands payment to restore access. It has caused significant disruptions in industries such as healthcare and education.
4. Insider Threats
Employees or contractors with authorized access may misuse their privileges intentionally or unintentionally, leading to data breaches or system damage.
5. Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
DoS attacks overwhelm a system with excessive traffic, rendering it unavailable to legitimate users. This can lead to financial losses and tarnished reputations for businesses.
Cybersecurity in Key Areas
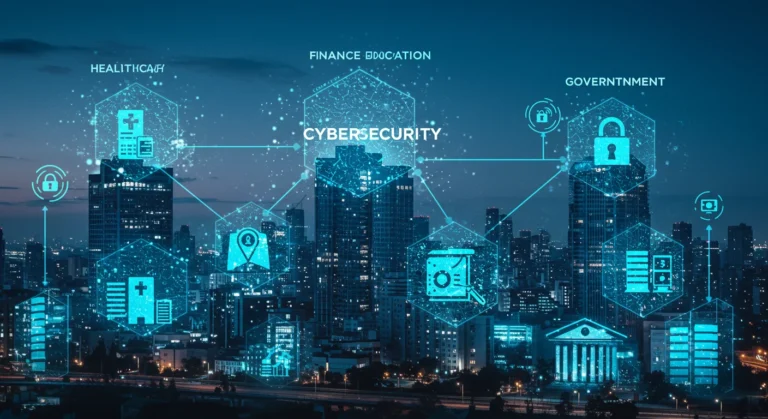

1. Healthcare
Healthcare systems store patient records and medical histories, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Cybersecurity ensures that sensitive patient data remains confidential and systems are protected from disruptions.
2. Finance
Banks and financial institutions are highly vulnerable to cyber threats. Cybersecurity measures, such as two-factor authentication and encryption, protect financial transactions and prevent fraud.
3. Education
Educational institutions increasingly rely on online systems for teaching, learning, and administration. Cybersecurity safeguards these systems from attacks that could compromise sensitive student and staff data.
4. Government
Governments use cybersecurity to protect critical infrastructure, classified information, and public services. Strong cybersecurity strategies also help in mitigating cyber warfare risks.
Essential Cybersecurity Practices
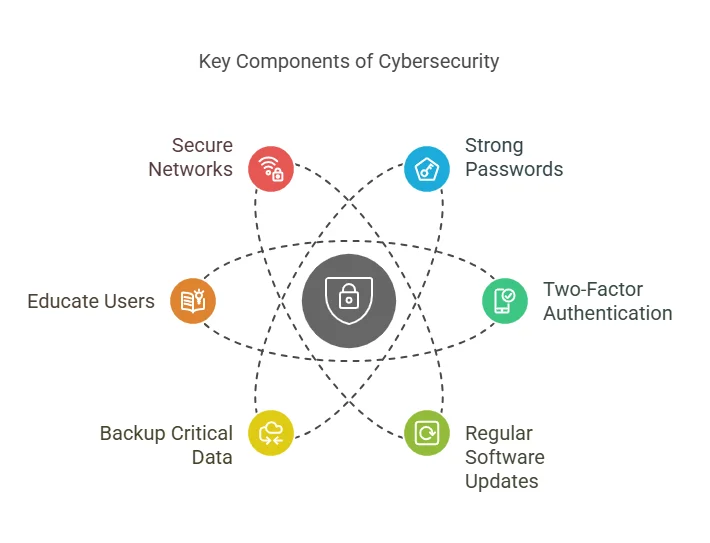
1. Use Strong Passwords
Passwords should be unique, long, and complex, combining letters, numbers, and special characters. Using password managers can help users manage their credentials securely.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA provides an additional layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through a secondary method, such as a code sent to their phone.
3. Regular Software Updates
Outdated software is a common target for attackers. Regular updates patch vulnerabilities and keep systems secure.
4. Backup Critical Data
Backing up data regularly ensures recovery in case of ransomware attacks or other data loss incidents. Backups should be stored securely in offline or cloud locations.
5. Educate Users
User awareness is a critical component of cybersecurity. Training employees and individuals about phishing, social engineering, and secure online practices can significantly reduce risks.
6. Secure Networks
Organizations and individuals should use firewalls and encryptions to protect their networks. Public Wi-Fi should be avoided for sensitive activities like online banking.
Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity

1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being used to enhance threat detection by analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying anomalies. It helps in predicting and preventing potential cyberattacks.
2. Biometric Authentication
Biometric systems, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, are gaining popularity as secure authentication methods.
3. Quantum-Resistant Encryption
With the rise of quantum computing, traditional encryption methods may become obsolete. Quantum-resistant algorithms are being developed to address this challenge.
4. IoT Security
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects billions of devices globally. Securing these devices is critical to preventing large-scale breaches.
The Cost of Ignoring Cybersecurity
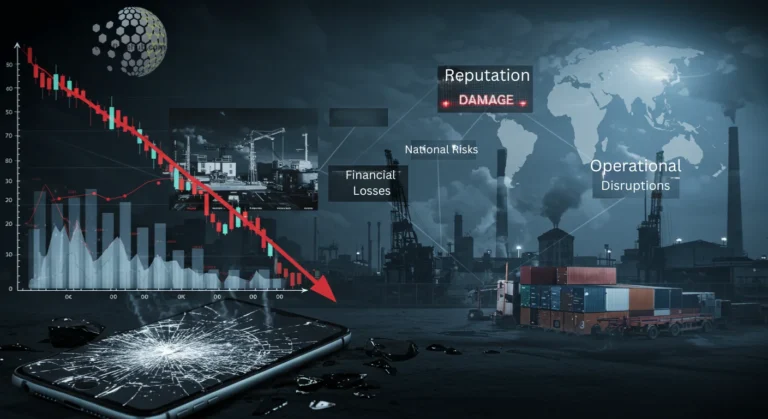
The absence of robust cybersecurity measures can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Financial Losses: Businesses may face lawsuits, fines, and loss of revenue due to breaches.
- Reputation Damage: A breach can erode trust and tarnish an organization’s reputation.
- Operational Disruptions: Attacks like ransomware can halt operations, causing downtime.
- National Risks: Cyberattacks on critical infrastructure can disrupt public safety and economic stability.
Future of Cybersecurity

As technology evolves, so do cyber threats. The future of cybersecurity lies in leveraging advanced technologies like AI and machine learning for proactive threat management. Governments and organizations must invest in research and development to stay ahead of attackers. Additionally, collaboration between countries and industries is essential to develop global standards and protocols for cybersecurity.
Protect your website with our SEO Solutions that include cybersecurity measures.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is a fundamental requirement in the modern digital world. It protects personal data, secures business operations, and ensures national security. By adopting best practices and investing in advanced technologies, we can create a safer digital environment. As cyber threats continue to evolve, a proactive approach is essential to safeguard our digital future.
